SELF ASSESSMENT - PRACTICE TEST
1. Which of the following wires has the greatest cross-sectional area?
a.9 AWG
b.14 AWG
c.22 AWG
d.30 AWG
2. What is the unit of measure for electrical pressure or electromotive force?
a.amps
b.ohms
c.volts
d.watts
3. Which of the following circuit configurations has the same amount of voltage drop across each of its components?
a.parallel
b.series-parallel
c.series
d.combination
4. As temperature increases, what happens to the current-carrying ability of a wire?
a.There is no change.
b.The wire can carry more current.
c.The wire can carry less current.
d.The wire can carry no current.
5. In a series circuit consisting of 3 resistors of 45 Ω each and a 50-V source, what is the approximate amount of heat produced?
a.16.6 W
b.18.5 W
c.135 W
d.150 W
6. In a two-branch parallel circuit containing one 30-Ω resistor in each branch and powered from a 10-V source, what is the total current flowing in the circuit?
a..33 A
b..67 A
c.40 A
d.60 A
7. Which of the following determines total power in a series circuit?
a.source voltage times the current
b.total voltage applied to the circuit
c.current flowing through a switch
d.average of the wattage consumed by each resistor
8. If a resistor suddenly decreases in value (resistance decreases), what will happen to the current through the resistor?
a.inductance
b.conductance
c.reactance
d.capacitance
9. What is the applied voltage on a circuit in which .5A is flowing and 10 W is generated?
a.2 V
b.5 V
c.20 V
d.50 V
10. Refer to Figure 1 on the Reference Sheet. Which drawing is the electrical symbol for a source of energy?
a.A
b.C
c.I
d.J
11. What is the classification of an AC circuit in which the capacitive reactance is 50 Ω, the inductive reactance is 30 Ω and the resistance is 100 Ω?
a.resistive
b.inductive
c.capacitive
d.resonant
12. When using a standard multimeter to measure AC voltage, what type of measurement will the multimeter indicate?
a.peak-to-peak
b.peak
c.average
d.rms
13. What happens to current flow in a capacitive circuit when the DC voltage across the capacitor is approximately equal to the source voltage?
a.Current flow is optimized.
b.Little current flows.
c.Current flow is maximum at the source.
d.Current flow is maximum at the capacitor.
14. What is the term used to describe the ability of a device to store energy in the form of an electrical charge?
a.inductance
b.conductance
c.reactance
d.capacitance
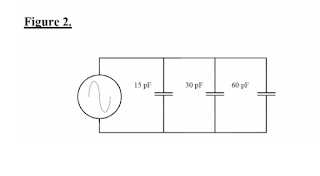
15. Refer to Figure 2. What is the total capacitance of this circuit?
a.15 pF
b.30 pF
c.105 pF
d.160 pF
16. If the distance between the plates of a capacitor decreases while all other components of the capacitor remain the same, what happens to the capacitance of the device?
a.increases
b.remains the same
c.decreases
d.varies
17. In mutual induction, what passes between conductors in order to create voltage?
a.radiation
b.magnetic flux
c.current flow
d.resistance
18. The Henry is the unit of measurement for which of the following properties?
a. reactanceb.
b.capacitancec.
c.resistance
d.induction
19. Which of the following devices can be used to test the windings of an inductor for continuity?
a.wattmeter
b.voltmeter
c.ohmmeter
d.Wheatstone bridge
20. Which of the following circuit conditions does a metal oxide varistor (MOV) protect against?
a.high voltage
b.high current
c.high circuit noise
d.high cross-talk
21. How should a fuse be installed in a circuit to insure proper operation?
a.parallel to the load
b.series with the load
c.in any way possible
d.at the ground point
22. In a parallel circuit operating with a source of 30 VAC, designed to carry a total current of 6 A, what happens to the protection device (fuse) when the resistance suddenly changes to 2 Ω?
a.closes
b.no change
c.shorts to ground
d.opens
23. How many watts are in 100 microwatts?
a..01 milliwatts
b..1 milliwatts
c.1.0 milliwatts
d.10 nanowatts
24. Which of the following is an appropriate use for a voltmeter?
a.To measure difference of potential
b.To measure current flow
c.To determine total resistance
d.To determine power output
25. What should be observed when connecting a voltmeter into a DC circuit?
a.rms
b.resistance
c.polarity
d.power factor
EXPLANATION OF PRACTICE TEST QUESTIONS:
1. (A) The larger the cross-sectional area of a wire, the greater the number of electrons it can carry. The American Wire Gauge (AWG) system provides guidelines on wire characteristics. The smaller the value of AWG, the greater the cross-sectional area of the wire. The 9 AWG wire will have the greatest cross-sectional area of any of the choices.
3. (A) In a series circuit, the current is equal at each point in the circuit and voltage is divided among the circuit components. In a parallel circuit, the voltage across each component is the same and the current is divided among the separate branches.
4. (C) Increasing temperatures cause electrons to be more active. The random nature of the increased activity causes collisions between thermally excited electrons and current carrying electrons. The collisions tend to disrupt the flow of electrons through the circuit. This disruption reduces the net current flow.
5. (B) Resistive elements in a circuit dissipate energy in the form of heat. Resistors connected in series are added to get total resistance. The power formula P = IE is used to determine the power used. First, use Ohm’s law to find the current (I).
• I = E/R = 50/135 = .37 amps
The power dissipated in heat can then be found using the power formula:
• P = IE = .37 * 50 = 18.5 watts
6. (B) Because the voltage drop across each component of a parallel circuit is the same, Ohm’s law can be used to find the current in each branch. The total current is then found by adding the current in each branch. Since in this case, the branches have equal resistance, simply find the current in one branch and multiply by the number of branches.
• Current in one branch: I = E/R = 10/30 = .333 amps per branch
• Total current of the parallel circuit: .333 amps * 2 branches = .67 amps
7. (A) The total power consumed in any circuit is a function of the power formula:
• Power = current (I) times voltage (E) or P = IE
8. (A) According to Ohm’s law, I = E/R, current has an inverse relationship with resistance. As resistance (R) decreases, current (I) increases.
9. (C) Use the power formula, P = IE, to find this answer. Solving for E:
• E = P/I = 10/.5 = 20W.
10. (C) The symbol for an energy source, in this case a battery, is symbol I.
11. (C) In a reactive circuit, the higher value of reactance will determine whether the circuit is capacitive or inductive. Here, the capacitive reactance is higher than the inductive reactance. Therefore, the circuit is capacitive.
12. (D) Electricity delivered to a wall outlet is stated in terms of rms voltage. A standard multimeter provides a reading of AC voltage in terms of rms.
13. (B) When a DC voltage is applied across a capacitor, there will be an initial flow of current. As the voltage across the capacitor charges up to the value of the source voltage, current flow will slowly decline. At the point where the voltage is approximately equal, all current in this circuit will stop flowing because there is no difference of potential.
14. (D) A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy.
15. (C) Capacitors in parallel are measured like resistors in series. Add the three capacitors to get the total capacitance of the circuit.
• 15 pF + 30 pF + 60 pF = 105 pF
16. (A) The value of a capacitor (capacitance) can be increased by increasing the surface area of the plates, increasing the value of the dielectric constant, or decreasing the distance between the plates.
17. (B) Magnetic flux is created as alternating current changes direction and causes lines of flux to vary in the magnetic field. As the lines of flux vary, they cause current to flow in nearby conductors.
18. (D) The Henry is a unit of measure for induction.
19. (C) Ohmmeters are used for testing continuity. Inductor windings are usually coils of wire and if not broken, can be tested with an ohmmeter for continuity.
20. (A) MOVs react very quickly to over-voltage conditions. When the voltage threshold of a MOV is exceeded, it instantly acts as a conductor, shorting the transient spike to ground. MOVs are commonly used to protect equipment that is attached to a transmission line.
21. (B) A fuse responds to an over-current condition by opening. This separates the source from the circuit in the event of an overload. Therefore it should be connected so that it is between the source of energy and the circuit—in series with the load.
22. (D) A circuit designed to work with 30 volts at 6 amps has a load resistance of 5 Ω (Ohm’s law). If the load resistance drops to 2 Ω, the circuit current will increase to 15 amps (Ohm’s law) if there is no way to stop it. If the protection device (see question 21) works properly, it will open a circuit if current goes beyond its designed current carrying ability.
23. (B) 100 microwatts = 100 * 10-6 watts = .0001 watts = 0.1 milliwatts.
24. (A) Voltmeters measure difference of potential in electrical circuits.
25. (C) Polarity is of major importance in direct current circuits. Voltmeters are sensitive to polarity when making measurements in DC circuits. Correct placement of leads is very important when making these kinds of measurements.

Very good information about electrical TECHNOLOGY
ReplyDeleteThanks for sharing your blog with us I am very inspired by your article kindly share some knowledge about Emergency Electrician want to know about it
ReplyDelete